Gout

What is Gout?
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis marked by sudden, intense pain and swelling in the joints, often affecting the big toe. It occurs when uric acid levels in the blood become elevated, leading to the formation of sharp urate crystals within the joint. This buildup causes painful flare-ups, typically accompanied by redness and tenderness, which can last for days and sometimes recur over time.
Gout is both a painful and potentially progressive condition that, when untreated, may lead to more frequent flares and long-term joint damage.
What causes Gout?
Gout is caused by an excess of uric acid in the bloodstream, known as hyperuricemia. Uric acid is a byproduct created when the body breaks down purines, which are naturally occurring substances found in our cells and certain foods. Normally, uric acid dissolves in the blood, passes through the kidneys, and is excreted in urine. However, when the body either produces too much uric acid or the kidneys do not eliminate it efficiently, uric acid builds up in the blood.
This excess uric acid then begins to crystallise, forming sharp, needle-like urate crystals. These crystals deposit within joints and surrounding tissues, triggering a strong inflammatory response from the immune system. This response leads to the characteristic pain, swelling, and redness associated with gout flare-ups. Over time, repeated crystal deposits can damage joint tissues and lead to chronic arthritis if not managed effectively.
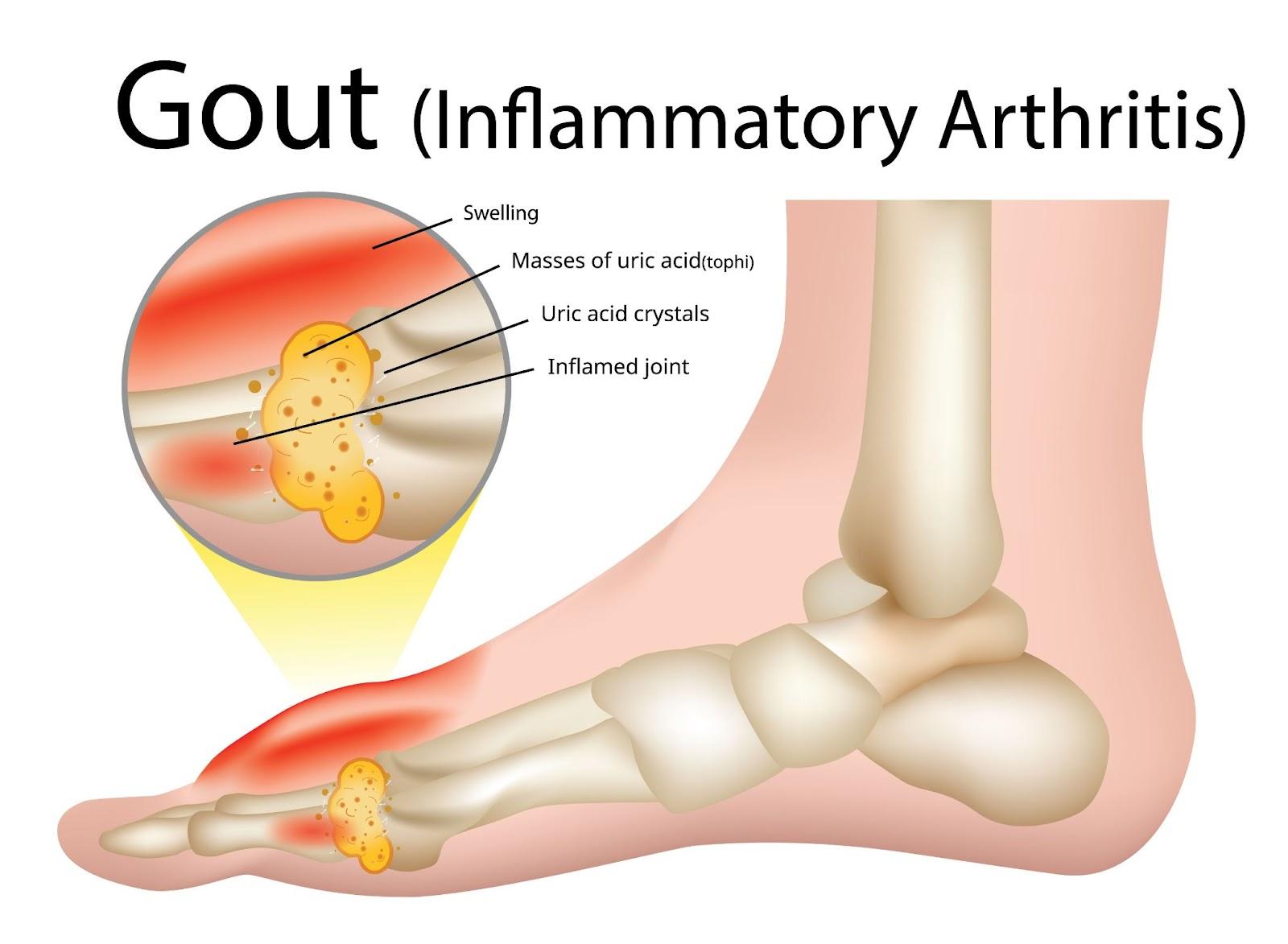
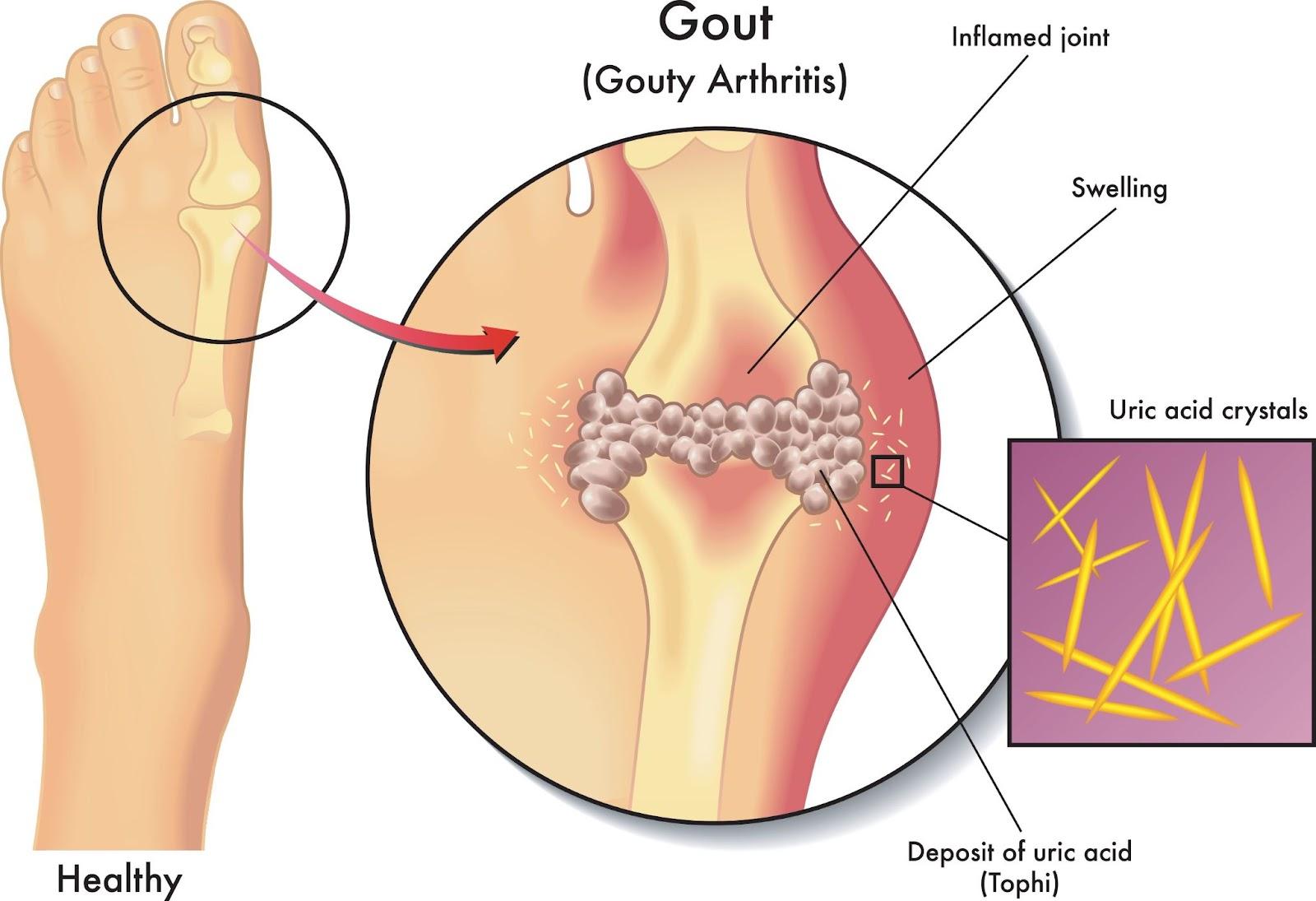
What are the symptoms of Gout?
Gout symptoms often come on suddenly and are usually severe, with many individuals experiencing flare-ups at night. These symptoms can significantly affect daily activities and comfort levels, particularly during an active flare.
- Intense joint pain: typically affects the big toe but can occur in other joints, including ankles, knees, elbows, wrists, and fingers.
- Lingering discomfort: even after the most severe pain subsides, joint discomfort can persist for days or even weeks.
- Swelling and redness: the affected joint often becomes swollen, tender, warm, and visibly red.
- Limited range of motion: as gout progresses, joint movement may become restricted due to pain and inflammation.
These symptoms may vary in intensity and frequency, but without proper treatment, flare-ups can become more frequent and severe over time.
Who is at risk of Gout in Singapore?
In Singapore, certain individuals are more susceptible to developing gout due to a combination of lifestyle, genetic, and health factors.
- Dietary choices: frequent consumption of foods high in purines, such as red meat, seafood, and sugary drinks, can increase uric acid levels.
- Alcohol consumption: regular intake of alcohol, particularly beer, is associated with higher uric acid levels.
- Obesity: excess body weight increases the body’s production of uric acid and decreases the kidneys’ ability to eliminate it efficiently.
- Chronic health conditions: conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and kidney disease elevate the risk of hyperuricemia, contributing to gout.
- Genetics: a family history of gout increases one’s likelihood of developing the condition.
- Age and gender: Gout is more common in men than women, although the risk increases in women post-menopause.
- Medications: certain medications, including diuretics and low-dose aspirin, can increase uric acid levels.
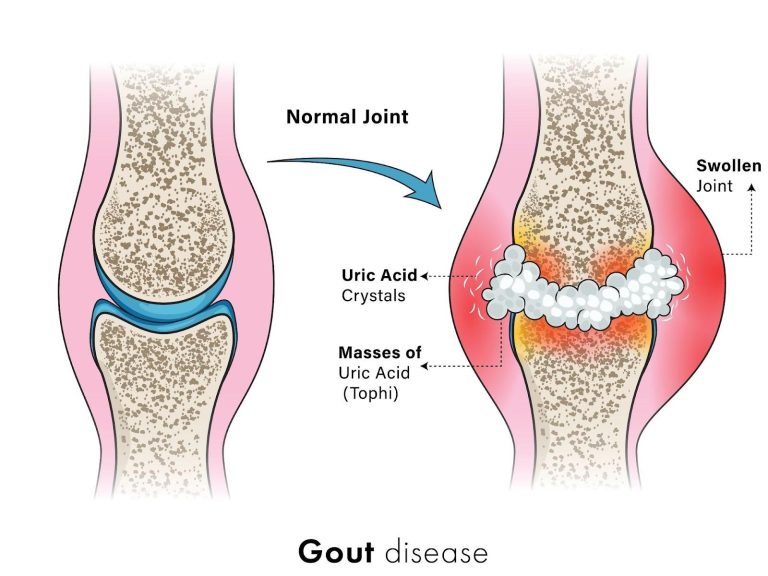
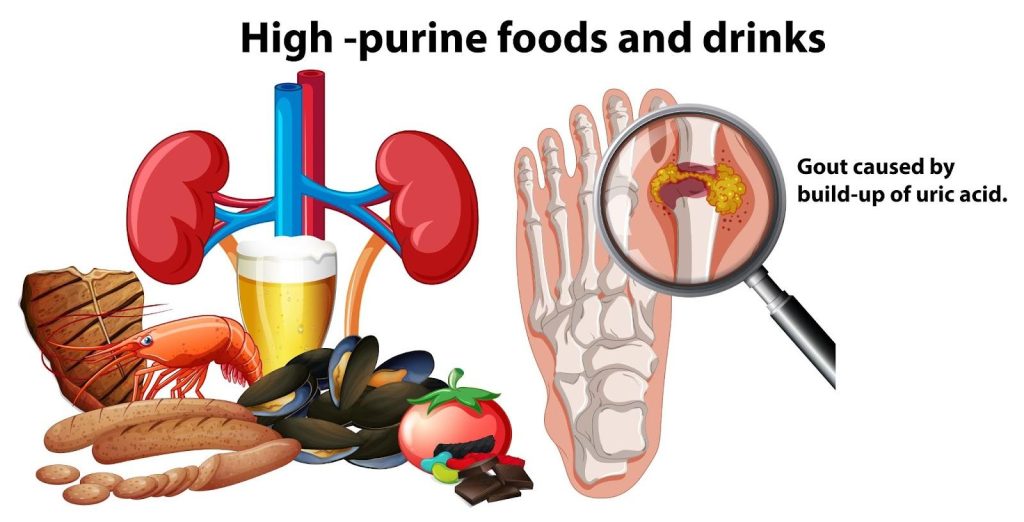
How is Gout diagnosed?
At Cove Orthopaedics, our team of experts utilise a comprehensive approach to assess the symptoms of gout. Here is how we approach the diagnostic process:
- Medical history and physical examination: we begin by discussing your symptoms and medical history and examining the affected joint for signs of inflammation and tenderness.
- Joint fluid analysis: a sample of fluid from the affected joint is taken to check for urate crystals under a microscope, which is a definitive method for diagnosing gout.
- Blood test: to measure the levels of uric acid in your blood, though we consider this alongside other findings, as high uric acid levels alone don’t confirm gout.
- Imaging tests: in some cases, we utilise advanced imaging techniques, such as ultrasound or dual-energy CT scans, to detect urate crystals.
What are the treatment options for Gout in Singapore?
At Cove Orthopaedics, we believe in a multi-faceted approach to managing gout, tailored to each patient’s needs and lifestyle. Our goal is to alleviate pain during acute attacks, prevent future flares, and improve overall joint health.
- Medications for acute flares: to quickly relieve pain and inflammation during a gout attack, we may prescribe nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, or corticosteroids.
- Urate-lowering therapy: to prevent future attacks, we often recommend medications such as allopurinol or febuxostat, which reduce uric acid production, helping to maintain lower levels long-term.
- Lifestyle modifications: our team provides guidance on dietary adjustments, hydration, and weight management to reduce uric acid levels naturally. Simple changes can make a significant impact in reducing flare-ups.
- Patient education and preventive care: we empower patients with knowledge about their condition, offering preventive strategies to minimise the risk of future attacks and protect joint health.
- Regular monitoring and follow-up: we believe in staying connected to track progress, adjust treatments as needed, and ensure you’re managing gout effectively in the long term.
At Cove Orthopaedics, we work closely with you to create a comprehensive gout management plan, combining medical treatment and lifestyle support to help you live pain-free and fully active.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of gout or need guidance on managing it effectively, schedule a consultation with Cove Orthopaedics today for personalised care and support.
Frequently asked questions
Can gout be cured?
While there is no definitive cure for gout, it can be effectively managed through medications and lifestyle changes to reduce uric acid levels, thereby preventing future flare-ups.
How can I prevent gout attacks?
Preventive measures include maintaining a healthy diet low in purines, staying hydrated, limiting alcohol intake, and adhering to prescribed urate-lowering medications.
Are there specific foods I should avoid if I have gout?
Yes, it’s advisable to limit consumption of red meats, organ meats, certain seafood (like anchovies and sardines), and sugary beverages, as they can increase uric acid levels.
Can gout affect multiple joints simultaneously?
While gout commonly starts in one joint, especially the big toe, it can progress to affect multiple joints over time if not properly managed.
How long does a gout flare typically last?
Gout flares usually last from a few days to two weeks, with the most intense pain occurring in the first 24 to 48 hours.
Are there any long-term complications associated with gout?
Chronic gout can lead to joint damage, the formation of tophi (deposits of urate crystals), and an increased risk of kidney stones if not adequately treated.
Is it safe to exercise during a gout flare?
It’s recommended to rest the affected joint during a flare to reduce pain and swelling; however, regular low-impact exercise between flares can help manage gout.
Can women develop gout?
Yes, while men are more commonly affected, women, particularly after menopause, can also develop gout.
Does dehydration influence gout attacks?
Dehydration can increase uric acid concentration in the blood, potentially triggering gout flares; thus, maintaining adequate hydration is important.