Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
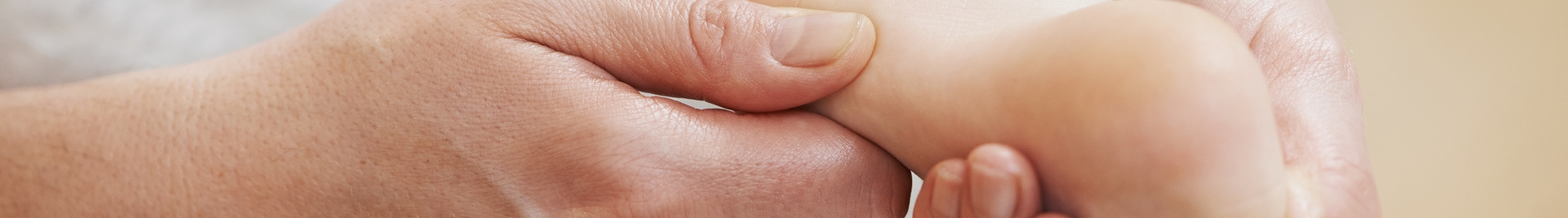
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when there is increased pressure or compression on the median nerve as it travels through the carpal tunnel in the wrist, one of the main nerves in the hand. This nerve controls the muscles surrounding the base of the thumb, and is what gives our thumb, index, middle and ring fingers feeling.
The median nerve is a nerve that travels down the arm and forearm, passes through the carpal tunnel at the wrist, and goes into the hand. The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway in the wrist that is surrounded by bones (carpal bones) and ligaments. Hence, when the median nerve is compressed, it can cause pain, numbness, tingling and weakness in the hand and arm.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS?
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome include:
- Numbness and tingling, mainly in the thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers
- Numbness or tingling that may travel up from the wrist and up to the arm
- Occasional electric shock sensations that radiate to the thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers
- Weakness in the hand and may drop things more often
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES AND RISK FACTORS?
Causes and risk factors of carpal tunnel syndrome include:
- Pressure on the median nerve
- Injury to the wrist, such as a fracture
- Medical conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes
- Heredity such as a smaller carpal tunnel running in the family
- Gender, where females are more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome
- Repetitive wrist motions such as repeated flexing of the wrist and gripping motions
- Obesity which increases your risk
- Pregnancy, where hormonal changes may cause swelling of the carpal tunnel
WHAT IS THE DIAGNOSIS?
A history of the injury and a physical examination of your hand will be conducted by the Doctor. He will check on the motion of your wrist and test if there is any difference in the feeling in your fingers.
Imaging tests such as an x-ray may be taken to eliminate conditions such as a fracture, and an electromyography to identify if you have suffered any nerve or muscle damage.
WHAT ARE THE TREATMENT OPTIONS?
Nonsurgical treatment options for carpal tunnel syndrome include:
- Resting your wrist and reduce activities that involve gripping and flexing of the wrist
- Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen) to relieve pain and reduce inflammation
- Application of ice packs to reduce swelling
- Wearing a splint at night to keep your wrist in a straight position
- Steroidal injections such as corticosteroid directly into the carpal tunnel to reduce inflammation and swelling
Should nonsurgical treatments fail to improve your symptoms, surgery may be recommended. Surgical options include:
- Endoscopic carpal tunnel release
During this procedure, tiny incisions will be made at your hand or wrist and a mini camera will be inserted to look inside your carpal tunnel, known as an endoscope. He will then make a cut at your carpal ligament to increase the size of the tunnel and decreases pressure on the median nerve.
- Open carpal tunnel release
During this procedure, a small incision will be made directly over the carpal tunnel in the palm of your hand and cut the carpal ligament. This will increase the size of the tunnel and decreases pressure on the median nerve.
WHAT IS THE RECOVERY PROCESS AFTER CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME SURGERY?
After surgery, it is normal for your hand to feel sore and weak with some swelling. it is recommended that you start moving your fingers to reduce stiffness by doing gentle stretching exercises. Do expect to wear a splint or wrist brace for several weeks.
Your grip should return around 2 to 3 months after surgery, but if your condition was severe, it can take up to 6 to 12 months for your strength to return. Do seek advice from your doctor when you may resume regular activity and return back to work.
WHAT ARE THE RISKS AND COMPLICATIONS OF THE SURGERY?
The most common risks of a carpal tunnel surgery includes:
- Incomplete release of the ligament
- Bleeding
- Wound infection
- Nerve or blood vessel injury