De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
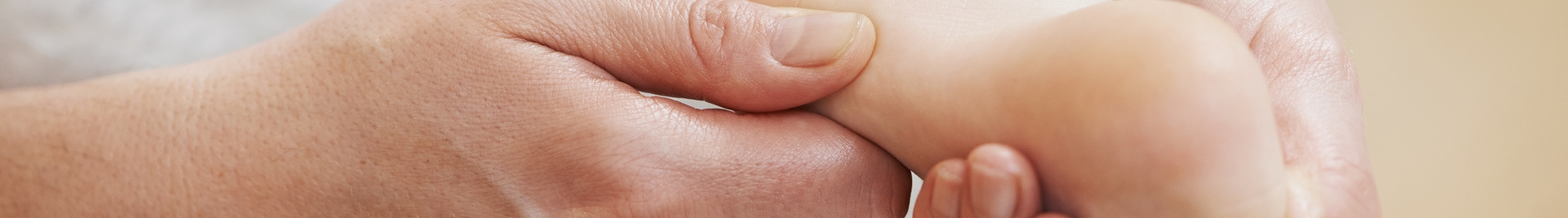
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis is a condition in which a patient feels pain at the base of the thumb side of the wrist. With friction from the repetitive movements of the wrist, this causes the tendons in our wrist to be constricted in a tight tunnel known as the tendon sheath, leading to pain.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS?
Symptoms of De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis include:
- Pain near the base of your thumb
- Swelling near the base of your thumb and your wrist
- Difficulty with activities involving moving your thumb and wrist, such as grasping, pinching or turning the wrist
- A “sticking” or “catching” sensation in your thumb when moving it
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES AND RISK FACTORS?
The main cause of De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis is the overuse of the wrist. Normally, when we move our wrist to do daily actions such as gripping, pinching or flexing, the tendons in our wrist make gliding motions through a tight tunnel (tendon sheath) located at the base of the thumb that allows for smooth movement and action. However, overuse of the wrist may cause irritation in the tendon sheath, resulting in inflammation and swelling that constricts the tendons, leading to De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis.
Other causes and risk factors of De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis include:
- Direct injury to the wrist or tendon which causes scar tissue to form, and this limits the movement of the tendons
- Inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis
- Age- 30 years and above have a higher risk
- Gender- women have a higher risk
- Pregnancy
- Occupation or hobby that involves repeated use of the wrist
WHAT IS THE DIAGNOSIS?
A history of the injury and a physical examination of your hand will be conducted by the Doctor. He will get you to do the Finkelstein test, where you will make a fist with the affected hand with fingers over the thumb. In a fist position, you will bend your wrist downwards in a shaking motion. should this cause pain at the base of your thumb, it indicates De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis.
WHAT ARE THE TREATMENT OPTIONS?
Early treatment is key to improve your condition. Nonsurgical treatment options include:
- Icing the affected area
- Medications for pain relief (acetaminophen) and to reduce inflammation (ibuprofen)
- Steroid injections such as corticosteroid directly into the tendon sheath to reduce swelling
- Wearing a splint at night to keep your thumb and wrist in a straight position
Should nonsurgical treatments fail to reduce your symptoms, surgery may be recommended. During surgery, your tendon sheath will be cut open to release the pressure and allow for smooth gliding of the tendons.
Physiotherapy for your hand may be required to strengthen your hand muscles and help you prevent future problems with your wrist.