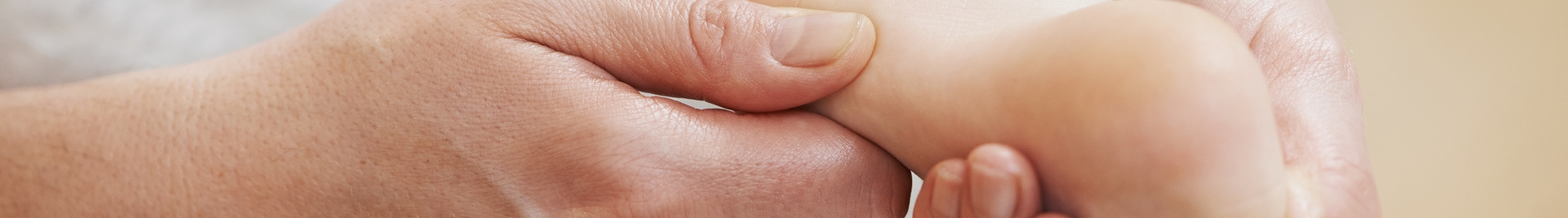
Tendonitis of the Wrist
Wrist tendonitis is the inflammation of the tendons in the wrist. These tendons are thick, fibrous cords that connect muscle to bone. When there is injury or damage to the tendons, or when there is repeated motion of the wrist, this can cause them to rub against the bone and get inflamed.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS?
Some symptoms of wrist tendonitis include:
- Pain and stiffness in the wrist after a period of inactivity such as waking up in the morning
- Pain, tenderness and soreness of the wrist
- Swelling
- A “creaking” sound may be heard when moving the wrist
- Weakness in the wrist when performing actions such as gripping, flexing and typing and you may experience a decreased range of motion
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES AND RISK FACTORS?
Wrist tendonitis is mainly due to the overuse of the wrist, such as doing repetitive motions. Common activities of this include typing on a keyboard, writing and chopping ingredients when cooking.
Other risk factors include:
- Age
- Bone structure- having poorly aligned joints
- Sudden injury to the wrist
- Medical conditions such as diabetes or arthritis
- Poor wrist posture
WHAT IS THE DIAGNOSIS?
A history of the injury and a physical examination of the hand and wrist will be conducted by the Doctor. He will check for tenderness in your wrist, and do tests to rule out other possible conditions such as De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis (Finkelstein test).
Imaging tests such as an x-ray may be taken to rule out a fracture as the cause of pain, and may take an MRI scan to examine the tendonitis in detail.
WHAT ARE THE TREATMENT OPTIONS?
Common nonsurgical treatment for wrist tendonitis includes:
- Applying heat and ice to reduce swelling in the wrist
- Stretching exercises
- Medication for pain relief (acetaminophen) and to reduce inflammation (ibuprofen)
- Steroid injections (corticosteroid) to reduce inflammation
- Changes in lifestyle to reduce stress and overuse of the wrist
- A wrist splint to be worn during the night to keep your wrist in place and to let it heal
Should nonsurgical treatments fail to improve your symptoms or if your tendon is damaged, surgery may be recommended. During surgery, the tendon sheath will be cut to release the space between the tendon and bone through small incisions made in the wrist.